Physical Therapy Info Health Tips
Our Integrated Physical Therapy blog, your go-to source for physical therapy articles and holistic health information. We provide expert insights, practical physical therapy tips, and the latest developments in the field. Whether you're recovering from an injury, managing chronic pain, or looking to improve your overall well-being, our physical therapy blog covers a variety of helpful topics.
Our goal is to empower you with the information you need to take an active role in your health and recovery. Ready to schedule an appointment and take control of your health? Contact Integrated Physical Therapy at 305-967-8976.
Physical Therapy Guide to Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Physical Therapy Guide to Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Often called a stiff or “frozen shoulder,” adhesive capsulitis occurs in about 2% to 5% of the American population. It affects women more than men and is typically diagnosed in people over the age of 45. Of the people who have had adhesive capsulitis in 1 shoulder, it is estimated that 20% to 30% will get it in the other shoulder as well. Physical therapists help people with adhesive capsulitis address pain and stiffness and restore shoulder movement in the safest and most effective way possible.
What is Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)?
Adhesive capsulitis is the stiffening of the shoulder due to scar tissue, which results in painful movement and loss of motion. The actual cause of adhesive capsulitis is a matter of debate. Some believe it is caused by inflammation, such as when the lining of a joint becomes inflamed (synovitis), or by autoimmune reactions, where the body launches an "attack" against its own substances and tissues. Other possible causes include:
- Reactions after an injury or surgery
- Pain from other conditions, such as arthritis, a rotator cuff tear, bursitis, or tendinitis, that has caused a person to stop moving the shoulder
- Immobilization of the arm, such as in a sling, after surgery or fracture
Often, however, there is no clear reason why adhesive capsulitis develops.
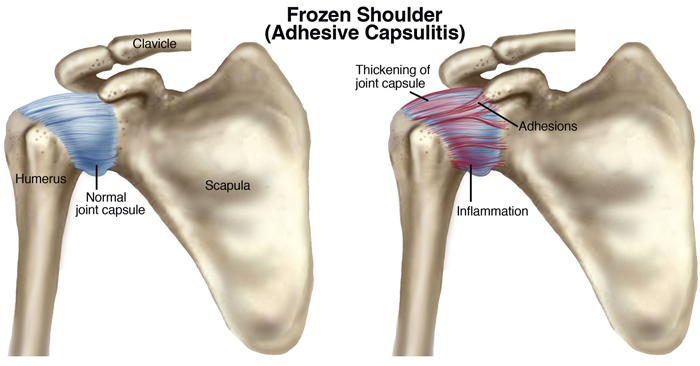
How Does It Feel?
Most people with adhesive capsulitis have worsening pain and a loss of movement. Adhesive capsulitis can be broken down into 4 stages; your physical therapist can help determine what stage you are in.
Stage 1: "Prefreezing"
During stage 1 of its development, it may be difficult to identify your problem as adhesive capsulitis. You've had symptoms for 1 to 3 months, and they're getting worse. Movement of the shoulder causes pain. It usually aches when you're not using it, but the pain increases and becomes "sharp" with movement. You'll begin to limit shoulder motion during this period and protect the shoulder by using it less. The movement loss is most noticeable in "external rotation" (this is when you rotate your arm away from your body), but you might start to lose motion when you raise your arm or reach behind your back. Pain is the hallmark feature of this stage; you may experience pain during the day and at night.
Stage 2: "Freezing"
By this stage, you've had symptoms for 3 to 9 months, most likely with a progressive loss of shoulder movement and an increase in pain (especially at night). The shoulder still has some range of movement, but it is limited by both pain and stiffness.
Stage 3: "Frozen"
Your symptoms have persisted for 9 to 14 months, and you have a greatly decreased range of shoulder movement. During the early part of this stage, there is still a substantial amount of pain. Toward the end of this stage, however, pain decreases, with the pain usually occurring only when you move your shoulder as far you can move it.
Stage 4: "Thawing"
You've had symptoms for 12 to 15 months, and there is a big decrease in pain, especially at night. You still have a limited range of movement, but your ability to complete your daily activities involving overhead motion is improving at a rapid rate.
How Can a Physical Therapist Help?
Your physical therapist's overall goal is to restore your movement, so you can perform your daily activities. Once the evaluation process has identified the stage of your condition, your physical therapist will create an individualized exercise program tailored to your specific needs. Exercise has been found to be most effective for those who are in stage 2 or higher. Your treatment may include:
Stages 1 and 2
Exercises and manual therapy. Your physical therapist will help you maintain as much range of motion as possible and will help reduce your pain. Your therapist may use a combination of range-of-motion exercises and manual therapy (hands-on) techniques to maintain shoulder movement.
Home-exercise program. Your physical therapist will give you a gentle home-exercise program designed to help reduce your loss of motion. Your therapist will warn you that being overly aggressive with stretching in this stage may make your shoulder pain worse.
Your physical therapist will match your treatment activities and intensity to your symptoms, and educate you on the appropriate use of the affected arm. Your therapist will carefully monitor your progress to ensure a safe healing procedure is followed.
Pain medication. Sometimes, conservative care cannot reduce the pain of adhesive capsulitis. In that case, your physical therapist may refer you for an injection of a safe anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medication. Research has shown that although these injections don’t provide longer-term benefits for range of motion and don’t shorten the duration of the condition, they do offer short-term pain reduction.
Stage 3
The focus of treatment during phase 3 is on the return of motion. Treatment may include:
- Stretching techniques. Your physical therapist may introduce more intense stretching techniques to encourage greater movement and flexibility.
- Manual therapy. Your physical therapist may take your manual therapy to a higher level, encouraging the muscles and tissues to loosen up.
- Strengthening exercises. You may begin strengthening exercises targeting the shoulder area as well as your core muscles. Your home-exercise program will change to include these exercises.
Stage 4
In the final stage, your physical therapist will focus on the return of "normal" shoulder body mechanics and your return to normal, every day, pain-free activities. Your treatment may include:
- Stretching techniques. The stretching techniques in this stage will be similar to previous ones you’ve learned, but will focus on the specific directions and positions that are limited for you.
- Manual therapy. Your physical therapist may perform manual therapy techniques in very specific positions and ranges that are problematic for you. They will focus on eliminating the last of your limitations.
- Strength training. Your physical therapist will prescribe specific strengthening exercises related to any weakness that you may have to help you perform your work or recreational tasks.
- Return to work or sport. Your physical therapist will address movements and tasks that are required in your daily and recreational life.
Can This Injury or Condition Be Prevented?
The cause of adhesive capsulitis is debatable, with no definitive cause. Therefore, to date, there is no known method of prevention. The onset of the condition is usually gradual, with the disease process needing to "run its course." However, the sooner you contact your physical therapist, the sooner you will receive appropriate information on how to most effectively address your symptoms.
What Kind of Physical Therapist Do I Need?
All physical therapists are prepared through education and experience to treat people who have frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis. You may want to consider:
- A physical therapist who is experienced in treating people with orthopedic, or musculoskeletal, problems.
- A physical therapist who is a board-certified clinical specialist or who completed a residency or fellowship in orthopedic physical therapy, manual physical therapy, or specializes in the treatment of the upper extremity. This therapist has advanced knowledge, experience, and skills that may apply to your condition.
For more information about this and other topics, contact our offices:
- 305.967.8976 - North Miami, Hallandale Beach and Wynwood
- 954.458.5700 - Hallandale



Comments